Bitcoin's Layer 1, revered for its unparalleled security and decentralization, has faced scrutiny over its scalability, cost, and throughput limitations. These constraints catalyzed the emergence of alternative networks like Ethereum, designed with smart contracting capabilities at their core. However, the narrative is shifting. With the introduction of Layer 2 solutions that integrate DeFi functionalities to Bitcoin, it’s poised to expand its utility far beyond a store of value.
In this article, we delve into the intricacies of Bitcoin Layers, and explore some of the projects in the space we’re most excited about.
As a team that is continually researching new technologies and exploring promising narratives, we’re thrilled to expand our expertise in the Bitcoin economy and collaborate with key players building in this ecosystem.
The Bitcoin Problem
Before delving into the nuances of Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions, let's take a step back and understand the core concept of Layer 2s. A Layer 2 is built on top of the base chain (Layer 1) to improve scalability and transaction throughput.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are Layer 1 protocols, serving as the settlement layer for all transactions on their respective networks. Layer 2 solutions offer a way to increase transaction speeds and scale the network while benefiting from the security of the main chain.
While numerous Layer 2 solutions, such as rollups, side chains, and channels, are already building on Ethereum, and Bitcoin Layer 2s have been in development for some time, several projects are now closer to launching and expanding Bitcoin's utility. However, scaling Bitcoin presents unique intricacies that need to be addressed.
The most crucial requirement for a Bitcoin Layer 2 solution lies in deriving its security from Bitcoin's own security model, a task that proves challenging in practice. To effectively secure a Layer 2, Bitcoin must possess the computational capability to validate the behavior of the Layer 2. However, Bitcoin's current computational capacity falls short compared to Ethereum's Layer 2 solutions.
For instance, Ethereum rollups derive their security from the Layer 1 by either verifying a zero-knowledge proof (zk-rollup) or confirming a fraud proof (optimistic rollup). Nevertheless, there are ongoing proposals aimed at enhancing Bitcoin's functionality to enable the base layer to validate zk-Proofs submitted by rollups. Additionally, initiatives like BitVM strive to implement fraud proofs without necessitating alterations to the base layer.
While solutions are emerging to address this challenge, they bring their own set of architectural choices and leverage novel technologies to find viable solutions. As the development of Bitcoin Layer 2s progresses, the ecosystem will need to carefully evaluate the trade-offs and implications of each approach.
Bitcoin's Layer 2 solutions face unique challenges in trying to improve upon the base layer. These challenges revolve around three main goals: handling more transactions, maintaining robust security, and ensuring that the system remains decentralized. Here's a simpler look at each goal:
By focusing on these three areas, Bitcoin's Layer 2 aims to enhance the base layer's capabilities while adhering to the principles of scalability, security, and decentralization. This approach ensures that the network can grow and adapt to new demands without compromising on its core values.
In this section, we explore a few Bitcoin L2s that we’re excited about, and provide a quick overview of the project.
Overview: Stacks brings smart contracts and decentralized apps to Bitcoin using a unique Proof-of-Transfer (PoX) mechanism. Key Features:
Overview: Designed for fast and cost-effective micropayments on Bitcoin.
Key Features:
Overview: Introduces Ethereum-compatible smart contracts to Bitcoin.
Key Features:
Overview: Builds on BTC to EVM bridging technologies, offering a novel dual-token staking model via $HODL.
Key Features:
Overview: The first implementation using BitVM, focusing on scalable and efficient transaction processing.
Key Features:
Overview: Merges Proof-of-Stake with Bitcoin’s robustness, focusing on cross-chain functionalities to offer Bitcoin restaking.
Key Features:
Overview: Offers private and scalable off-chain Bitcoin payments.
Key Features:
Overview: Implements a zk-rollup model to improve transaction efficiency and security on Bitcoin.
Key Features:
Overview: An Ethereum-based Proof-of-Stake Layer 2 that uses Bitcoin as its core asset for staking and governance.
Key Features:
Overview: A zk-rollup solution that stores proofs and transaction data directly on Bitcoin's blockchain.
Key Features:
Overview: BOB is an Ethereum-based Layer 2 solution designed to integrate closely with Bitcoin, maintaining alignment with Bitcoin's principles.
Key Features:
Overview: Twilight offers a platform for deploying privacy-focused decentralized exchanges and other applications, using advanced cryptographic methods to ensure security and privacy.
Key Features:
…and more! Stay tuned for Part 2, where we'll delve into even more exciting projects emerging within the ecosystem.
As a forward-thinking infrastructure provider, Chorus One is thrilled about the immense potential of integrating DeFi functionalities into Bitcoin and witnessing its evolution beyond being a store of value. Engaging in in-depth research into promising new technologies and projects, we're excited to explore a new landscape beyond Proof of Stake-based networks.
We're actively collaborating with L2s to delve deeper into the ecosystem. If you're interested in learning more or getting involved with some of the projects we're working with, please reach out to us at staking@chorus.one. We'd be delighted to connect with you.
In blockchains that utilize Proof of Stake, staking allows users to receive rewards by locking tokens to aid in validating transactions and securing the network. Staking services lower barriers to entry by handling technical complexity. Users can stake any tokens without the need to run validators.
At Chorus One, we are happy to announce that we will provide Staking-as-a-Service (SaaS) solution to users at the Lava mainnet launch. Lava network is a protocol that serves as a gateway for applications to access trustworthy, secure, and swift RPC services. Unlike conventional methods that hinge on centralized or public RPC endpoints, Lava Network leverages a decentralized array of premier service providers.
At the cutting edge of blockchain accessibility, Lava provides a user-friendly and scalable solution to tackle the crucial requirement for an Access layer in the blockchain infrastructure. The network makes it very easy for blockchains and rollups to bootstrap a set of infrastructure providers, so users and developers can onboard smoothly.
Lava is an application-specific marketplace for decentralized blockchain Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) and APIs based on CosmosSDK. Lava is designed to enhance access scalability to various blockchains. This network has the ability to accommodate any RPC and API in a flexible manner,. Lava boasts of a lightning-fast network that is hyper-scalable, and permissionless with nearly 100% uptime.
A Remote Procedure Call, or RPC, is a lightweight software communication protocol, that allows for developers to run code that can be executed on servers remotely.
On Lava, blockchain and rollup developers can quickly bootstrap a network of infrastructure providers, without waiting for major providers to add support. The protocol's initial focus is directed towards RPC infrastructure, a service that aids developers to access over 30 diverse chains, from EVM to Cosmos.

In this section, we break down the different architectural elements of the Lava Network:
Specs - Specs, otherwise called Specifications, are the foundational blueprints for Lava's multichain support, outlined in JSON format. These specifications delineate the minimum requirements necessary for an API to function on Lava effectively. Through these specs, Lava identifies the supported chains and methods while also setting up the associated costs, prerequisites, and validations. Each time the ecosystem requires a fresh API, a new specification is seamlessly integrated. This flexible method seamlessly weaves modularity into the protocol, guaranteeing that Lava stays up-to-date and flexible.
Peer-to-Peer Lava SDK - The Lava SDK is a decentralized, peer-to-peer blockchain RPC for developers who are exploring the cross-chain functionality the ecosystem is offering. It offers a simplified setup for multi-chain RPC, where adding a new chain can be done with a few lines of code. The Lava-SDK is a JavaScript/TypeScript library that was built to provide decentralized access to all chains supported by the Lava ecosystem. It further provides necessary tools for server and online environments, simplifying the process of building decentralized applications and interacting with multiple blockchains.
Gateway - Lava Gateway is a user-friendly web platform for developers that provides instant access to blockchain data. The Gateway makes use of the Lava Server Kit to offer a hosted entry point for developers seeking RPC via the Lava Network. This setup enables users to handle and set up Web3 APIs using user-friendly controls right from their browser. While the Lava Server Kit and SDK offer enhanced control and permissionless features, the Lava Gateway grants similar entry to our base network along with extra conveniences like project management utilities and user accounts.

The Lava mainnet is scheduled to launch soon while the team focuses on delivering an easy, fast multi-chain experience. The team published their Tokenomics today, which is available here.
Token details for LAVA stakers:
• LAVA is used to reward infrastructure providers on Lava
• Providers can earn native tokens from chains/rollups supported by the network
• LAVA can be restaked to earn additional yield and lower security fees
• LAVA has a capped supply with deflationary mechanisms
Lava Network is a modular network that focuses on giving blockchains and rollups a performant and reliable access layer. RPC is the first supported use-case, but other services related to data access will be added soon e.g. indexing.
To read more about Lava Network, we recommend the official documentation available in docs.lavanet.xyz.
We currently support infrastructure for over 50 networks, and we're thrilled to announce that Chorus One will be providing staking services to users as the Lava team heads towards the mainnet.
Chorus One Ventures is an early investor in LAVA, and has been supporting the project since its inception. Chorus One’s impeccable reputation, along with its thorough risk management protocols and collaborations with insurance providers, highlights the priority placed on safeguarding, ensuring the security of your LAVA staking activities remains untarnished.
For any other questions or to stake LAVA with Chorus One, reach out to staking@chorus.one
Chorus One is one of the biggest institutional staking providers globally, operating infrastructure for 50+ Proof-of-Stake networks, including Ethereum, Cosmos, Solana, Avalanche, and Near, amongst others. Since 2018, we have been at the forefront of the PoS industry and now offer easy enterprise-grade staking solutions, industry-leading research, and also invest in some of the most cutting-edge protocols through Chorus Ventures. We are a team of over 50 passionate individuals spread throughout the globe who believe in the transformative power of blockchain technology.
The EigenLayer ecosystem has emerged as a crucial driver of innovation and expanding the capabilities of the Ethereum network. As a leading node operator, we have taken a strategic, Safety over Speed approach to identifying and onboarding some of the most exciting Actively Validated Services (AVSs) that are set to transform the industry.
Let's dive into the first batch of EigenLayer AVSs that Chorus One is registering:
1. EigenDA: Scaling Data Availability for Rollups [Onboarded]
At the heart of the scalability challenges faced by Ethereum lie the complexities of data availability. EigenDA aims to tackle this problem head-on by providing a secure and scalable data availability solution for optimistic and zero-knowledge (ZK) rollups. By leveraging the restaking primitive developed by EigenLabs, EigenDA empowers rollups to access lower transaction costs, higher throughput, and robust security across the EigenLayer ecosystem.
Why we onboarded EigenDA: As the first AVS to launch on the EigenLayer mainnet, and its impressive $1 billion in total value locked (TVL), we see immense potential in supporting EigenDA and positioning it as a preferred solution for leading Layer 2 ecosystems, including the OP Stack.
2. Brevis: Trustless Co-Processing for Data-Rich Applications [Onboarded]
Brevis belongs to a class of solutions that thrive within the EigenLayer ecosystem – co-processor networks. These specialized networks extend the functionality of a stack to handle computationally intensive tasks, such as verifying complex data points for decentralized applications (dApps).
Brevis tackles the challenge of "data-rich" use cases, where retrieving and validating on-chain data can be both time-consuming and costly. By leveraging a novel "propose-challenge" model, Brevis generates ZK proofs to ensure the accuracy of its results, empowering applications in DeFi, user-segment optimization, and beyond to operate in a truly trustless manner.
Why we onboarded Brevis: Our decision to onboard Brevis as its second AVS was driven by the project's open-source codebase and the alignment with the team's vision. As a modular and efficient solution, Brevis aligns perfectly with Chorus One's commitment to driving innovation and supporting the growth of the decentralized ecosystem.
3. Eoracle: Bringing Transparency and Security to Oracle Networks
One of the biggest hurdles in the crypto industry has been the "oracle problem" – the challenge of reliably and securely bringing real-world data onto blockchain networks. Eoracle aims to address this issue by creating an Ethereum-native oracle solution that leverages the decentralization, transparency, and security of the Ethereum network.
Why are we onboarding Eoracle: As the "Data Validator" AVS operated by Chorus One, Eoracle connects node operators to compute, validate, and publish off-chain data to dApps in a secure and trustless manner. By tapping into the Ethereum validator set through EigenLayer, Eoracle represents a crucial step towards building a more robust and reliable oracle infrastructure for the decentralized ecosystem.
4. Lagrange: Cryptographically secured proofs for the Multichain Future
Inspired by Ethereum’s Sync Committee, Lagrange’s State Committee seeks to provide a robust, scalable, and shared security solution for cross-chain interoperability. This works by enabling multiple protocols to derive security from a shared security zone made up of a single, dynamic set of Ethereum nodes. Operators can deploy the Lagrange State Committees in combination with restaking through EigenLayer, to address the challenges with current approaches to cross-chain interoperability.
Why we are onboarding Lagrange: As the first zero knowledge AVS on Eigenlayer, we are excited to work with an innovative solution like Lagrange. With 15+ committed professional operators and over $2 billion in pledged security by leading LRTs, we feel confident in supporting Lagrange in addressing the security question in cross-chain interoperability.
5. AltLayer: Bridging the Rollup Ecosystem
AltLayer offers two key services that are highly relevant to the Ethereum ecosystem. The first is their Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) solution, which enables the fast and customized deployment of rollups. The second, and more pertinent to Chorus One, is their "Restaked Rollups" – a vertically integrated suite of three AVSs that leverage EigenLayer's shared security to support decentralized rollups.
Why are we onboarding AltLayer: AltLayer's Restaked Rollup solution addresses key challenges facing decentralized rollups, such as the need for a decentralized sequencer (SQUAD), a robust verifier (VITAL), and fast finality (MACH). By onboarding this comprehensive suite of AVSs, starting with their MACH AVS in this iteration, we aim to provide critical infrastructure and support to the broader rollup ecosystem, accelerating the growth and adoption of scalable decentralized applications.
6. Witness Chain: Incentivizing Fraud Proofs for Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic rollups offer a promising path to Ethereum scalability, but their security properties have been limited by the lack of clear incentives for validators to diligently search for and submit fraud proofs. Witness Chain addresses this challenge with its Watchtower protocol – a programmable, trustless, and decentralized service that uses a novel "proof of diligence" mechanism to incentivize validators to support optimistic rollups.
Why are we onboarding Witness Chain: By onboarding Witness Chain as an AVS, we aim to continue our ongoing commitment to strengthening the security and decentralization of the L2 ecosystem, which is a crucial component of Ethereum's scalability roadmap. As optimistic rollups continue to gain traction, Witness Chain's services will play a vital role in ensuring the long-term viability and trust in these scaling solutions.
Stay tuned for Part 2 of this series, where we'll explore the additional exciting AVSs that Chorus One is onboarding to the EigenLayer network, further expanding the potential of the EigenLayer and Restaking ecosystem.
About Chorus One
Chorus One is one of the biggest institutional staking providers globally, operating infrastructure for 50+ Proof-of-Stake networks, including Ethereum, Cosmos, Solana, Avalanche, and Near, amongst others. Since 2018, we have been at the forefront of the PoS industry and now offer easy enterprise-grade staking solutions, industry-leading research, and also invest in some of the most cutting-edge protocols through Chorus Ventures. We are a team of over 50 passionate individuals spread throughout the globe who believe in the transformative power of blockchain technology.
EigenLayer recently upgraded to M2 Contract. This made it necessary for EigenPods created prior to this to be upgraded. So if your EigenPod was created prior to Stage 2, you will need to upgrade your EigenPod per the steps below. EigenPods that were created prior to M2 contract upgrades are required to have their balances reset to zero, then generate the proofs through the EigenLayer app in order to ensure proof accounting is accurate.
Note: This guide is useful for the native restaking users who want to delegate to Chorus One operator but don’t see any restaked tokens. This can happen when you restaked before the M2 upgrade. Following this guide you will start seeing your restaked tokens which can then subsequently be delegated to Chorus One
1. Go to https://app.eigenlayer.xyz/restake and connect your wallet

2. You will see a button to upgrade your EigenPod. Click Upgrade Eignepod
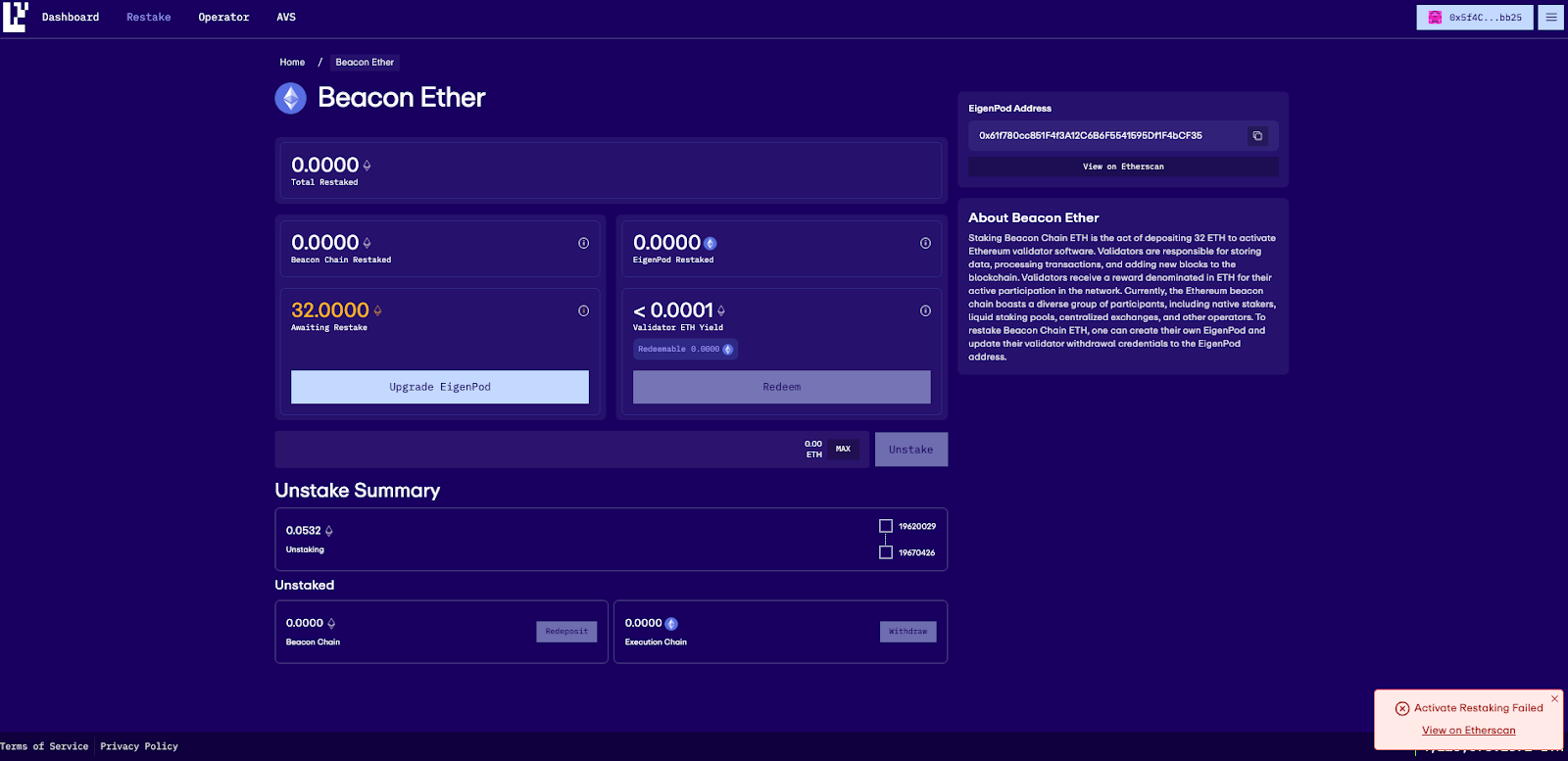
3. You will be shown a fee recipient warning, review the warning and click Continue


4. In case you have accrued any Consensus Rewards you might be asked to queue the withdrawal of the rewards before you can upgrade your EigenPod. Click Confirm.


5. Observe the Restaking Activated confirmation and explanation that Restaking will be available after the next beacon state update.


6. You can wait for the amount of time mentioned in the message. Come back later and hit the restake button to Restake your ETH

7. Once you restaked your ETH you can follow the steps in this delegation guide to delegate your restaked ETH to Chorus One operator

About Chorus One
Chorus One is one of the biggest institutional staking providers globally, operating infrastructure for 50+ Proof-of-Stake networks, including Ethereum, Cosmos, Solana, Avalanche, and Near, amongst others. Since 2018, we have been at the forefront of the PoS industry and now offer easy enterprise-grade staking solutions, industry-leading research, and also invest in some of the most cutting-edge protocols through Chorus Ventures. We are a team of over 50 passionate individuals spread throughout the globe who believe in the transformative power of blockchain technology.